When you are contracting your pelvic floor muscles, your back passage closes
The pelvic floor is not a large and powerful group of muscles; therefore do not expect to see or feel a lot of movement when contracting your muscles.
It is almost like closing your mouth, but at the other end of your body.
You must feel that your back passage closes as this is where the majority of the movement takes place.
Training the pelvic floor muscles takes concentration.
Avoid unnecessary movements
When exercising, it is important that you get the feeling that only the pelvic floor is working. Be aware that you:
- Do not tighten your buttocks
- Do not contract the muscles on the inside of your thighs
- Do not suck in your stomach or hold your breath
You can check if you are doing it right
You can with a couple of fingers on the perineum (area between the lower end of the vagina and back passage), feel the area become tight during a muscle contraction.
Or place the index finger and middle finger in the vagina, tighten the muscles and feel your vagina clamp around your fingers
You can also hold a mirror between your legs. Contract the muscles to see a movement around the urethra, vagina and back passage.
Adjust the severity of the exercises
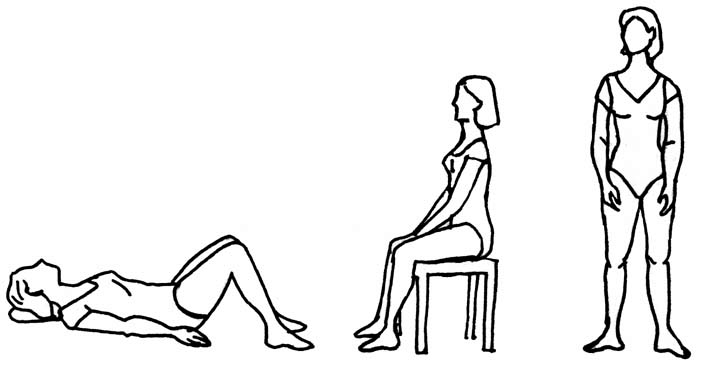
In the beginning it is easiest to train lying down on your back, tummy or side.
Later on you must train sitting, then in standing position. And finally in motion (e.g. jump and run). This is to increase the difficulty of the exercises and thereby increase the strength of the pelvic floor muscles.